Food chemistry is the study of the chemical processes underlying the structure, nutrition, taste, and aroma of foods, and the changes that occur to them when they are manipulated during preparation.
Food chemistry
Articles related to chemical components and interactions in food
Examples

Acetone
Chemical compound, the simplest ketone
Acidifier
Inorganic chemicals that either produce or become acid
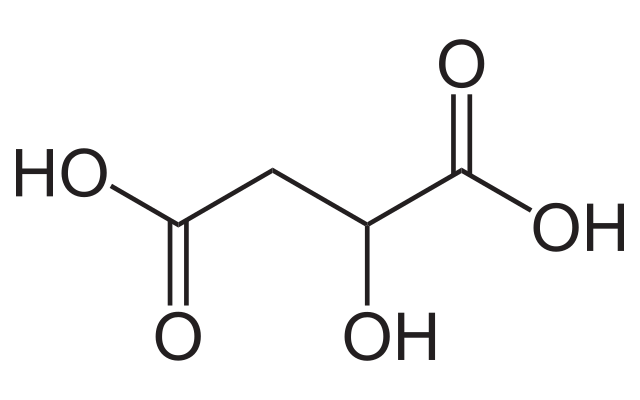
Acidulant
Food additive adding acid to food
Acidulated water
Water with low level of acid
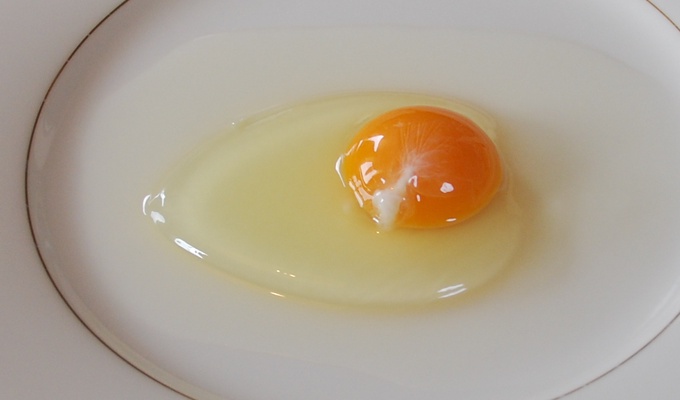
Albumen
clear liquid contained within an egg

Alcohol by volume
Measure of how much alcohol is in a beverage
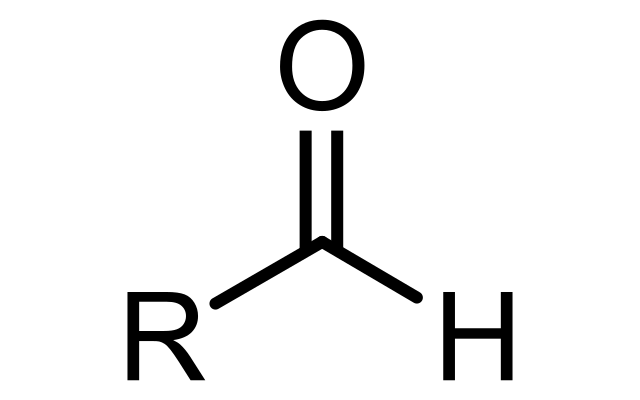
Aldehyde
organic compounds containing a functional group with the structure −CHO, consisting of a carbonyl center (a carbon double-bonded to oxygen) with the carbon atom also bonded to hydrogen and to an R group, which is any generic alkyl or side chain
Alkalescents
Alkali
basic, ionic salt of an alkali metal or alkaline earth metal chemical element
Alkali volatile

Alkaloid
class of naturally occurring chemical compounds
Alpha-amylase
Enzyme used to convert starch to sugar
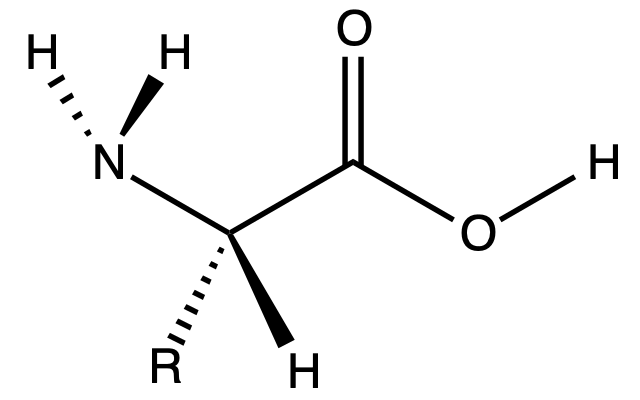
Amino acid
Organic compound, used to build proteins, essential for life
Amylase
Enzyme used to convert starch to sugar
Amylopectin
Complex carbohydrate; major component of starch
Amylose
Complex carbohydrate; major component of starch

Anthocyanin
Water soluble red, purple, and blue pigment in foods
Antioxidant
Molecule that inhibits the oxidation of other molecules

Arsenic
Chemical element with symbol As and atomic number 33
Artificial sweetener
Chemical that triggers sensation of sweetness
Base
Chemical property, opposite of acid
Brix
unit of measurement for sugar content of an aqueous solution
Butylated hydroxytoluene
Food preservative additive, also called BHT
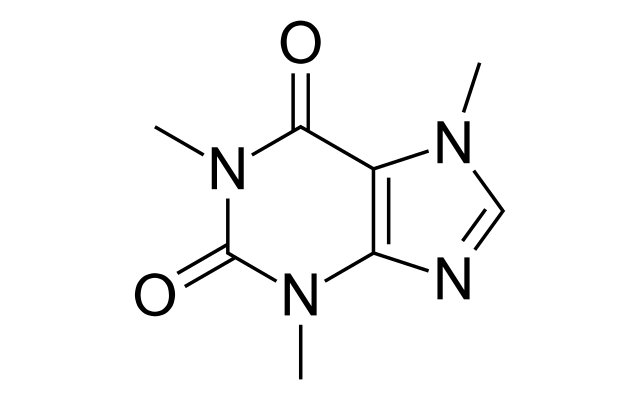
Caffeine
chemical compound
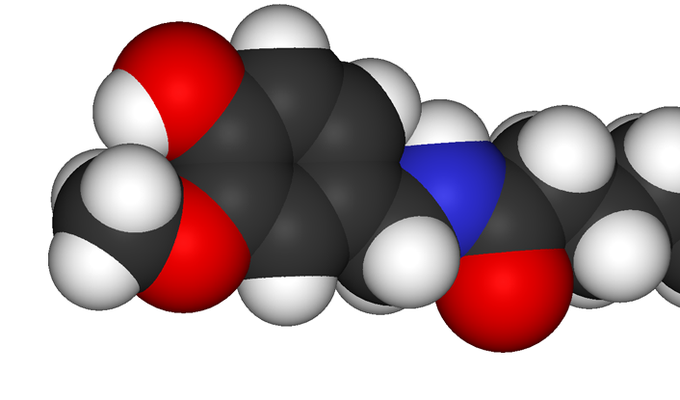
Capsaicin
Chemical compound responsible for sensation of spicy heat
Carbohydrate
Macronutrient, representing sugars, starches, and fiber
Cellulose
Indigestible carbohydrate in plants
Coagulate
Process of protein solidification
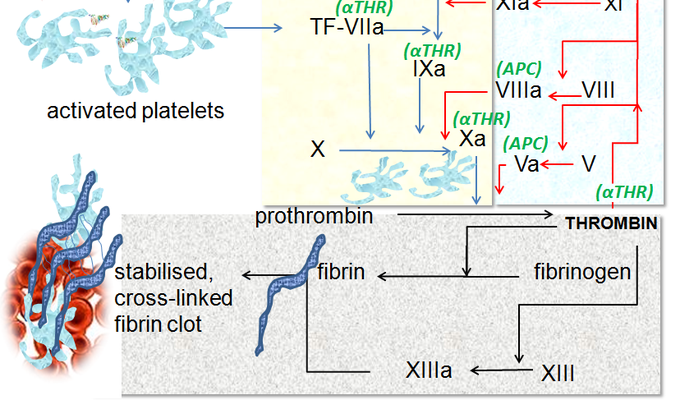
Coagulation
process in which the coagulation factors of the blood interact, ultimately resulting a clot
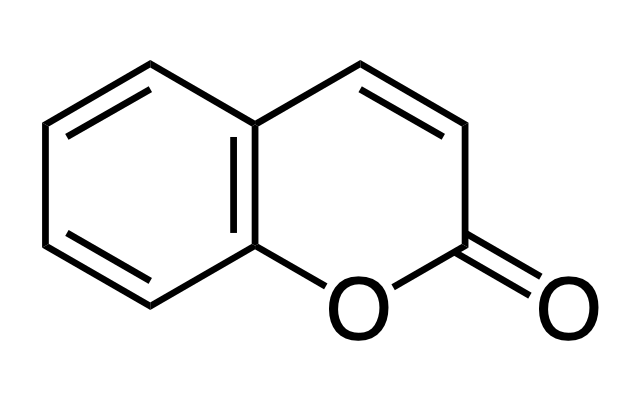
Coumarin
chemical compound
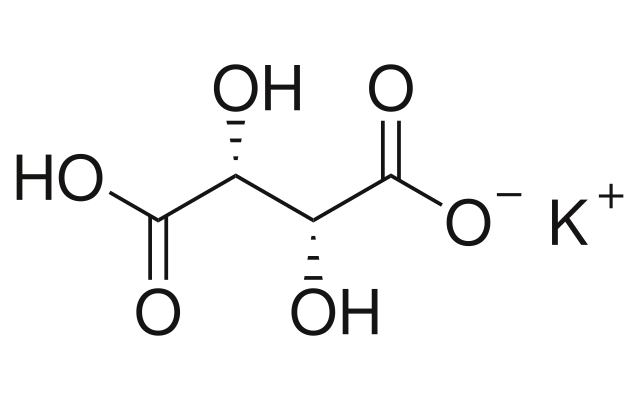
Cream of tartar
potassium acid salt of tartaric acid
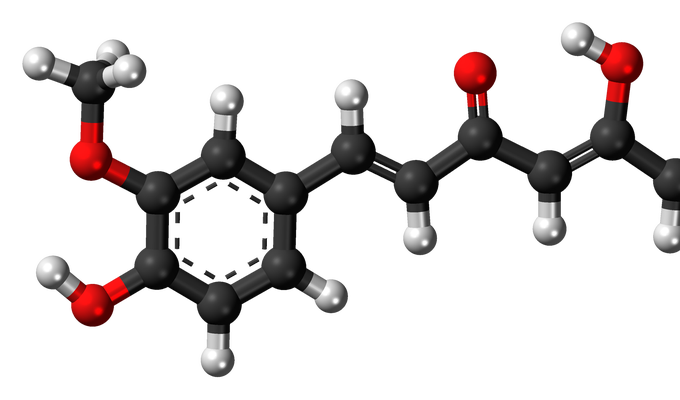
Curcumin
chemical compound, main yellow-orange-colored pigment and active principle of turmeric or curcuma
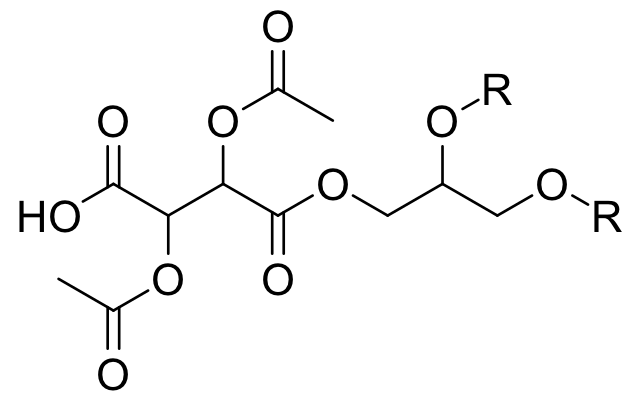
DATEM
food additive
Denature
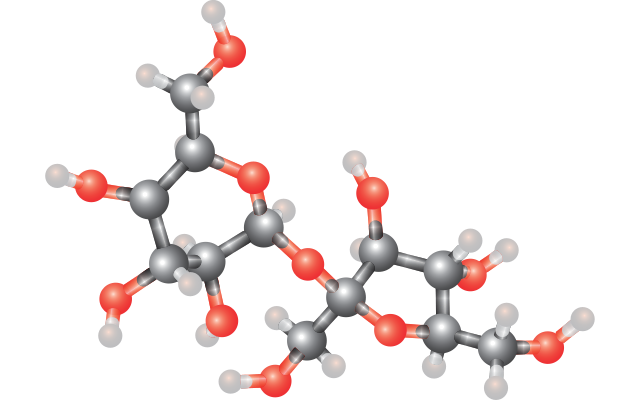
Disaccharide
complex sugar, formed when two monosaccharides are joined by glycosidic linkage
Emulsifier
Mixture of two or more liquids that are normally unmixable
Enzyme
large biological molecule that acts as a catalyst
Epimer
Pair of chemical compounds differing in one point
Essential oil

Extract
substance made by extracting a part of a raw material
Fat
Any triglyceride molecule found in foods, including oils and animal fats
Fatty acid
Building blocks of fats

Fiber
indigestible portion of food derived from plants
Flavonoid
chemical compound containing two or more aromatic rings, each bearing at least one aromatic hydroxyl and connected with a carbon bridge
Gliadin
class of proteins
Glutelin
Proteins found in grass, major component of gluten

Gluten
Protein composite found in wheat and related grains, including barley and rye

Humidity
amount of water vapor in the air
Hydrogen cyanide
Poisonous chemical compound
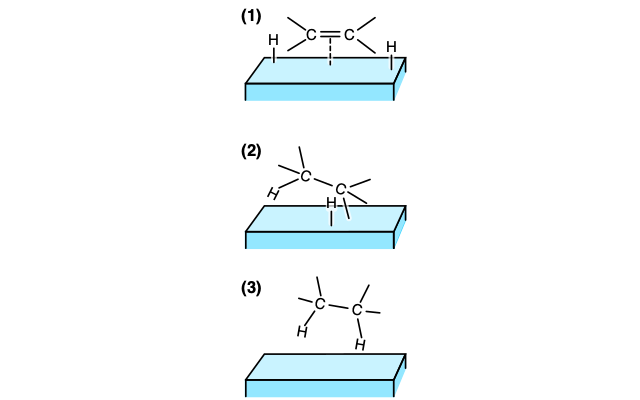
Hydrogenated
chemical reaction between molecular hydrogen and another compound or element, usually in the presence of a catalyst such as nickel, palladium or platinum
Hydrolyzed vegetable protein
food ingredient made by protein hydrolysis of plant protein with a meat-bouillon-like taste
Hygroscopic
Chemical property of absorbing moisture
Inversion
Invertase
class of enzymes that hydrolyze disaccharides
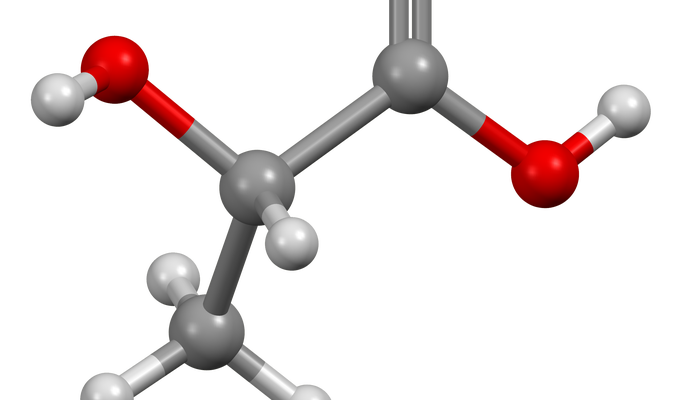
Lactic acid
Bacterial product with crucial role in yogurt, cheese, pickles, and sourdough
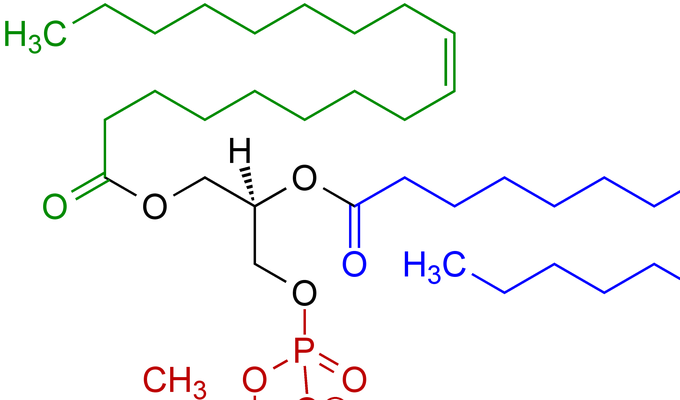
Lecithin
Naturally occuring emulsifier
Lipid oxidation
Reaction of fats with oxygen, leading to off flavors and odors

Lye
class of caustic compounds
Macronutrient
Nutrient required in large quantities for energy and health

Maillard reaction
Chemical reaction in roasting, baking, or frying
Menthol
Chemical present in mint plants with distinctive cooling sensation
Mixture
substance formed when two or more constituents are physically combined together
Modified starch
Starch modified with physical, chemical, or enzymatic processes
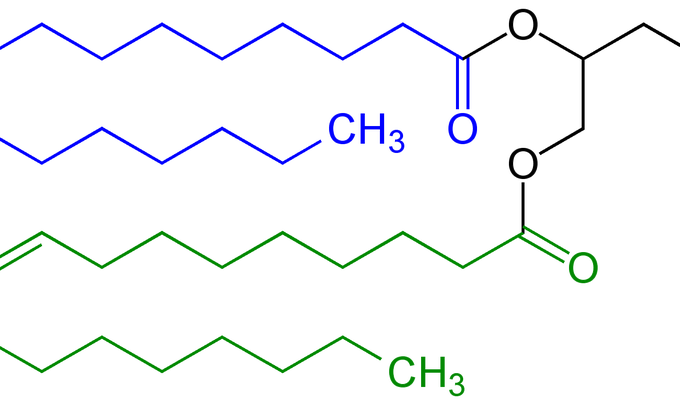
Mono- and diglycerides
emulsifier
Monosaccharide
simple sugars such as glucose and fructose
Monounsaturated fat
Dietary fat, associated with beneficial health effects

Mucilage
Viscous substance produced by plants and some microorganisms
Nigari
Magnesium chloride, used in production of tofu
Nitrosamines
Chemicals formed from nitrites, linked to cancer risk
Oleuropein
Bitter chemical compound found in olives
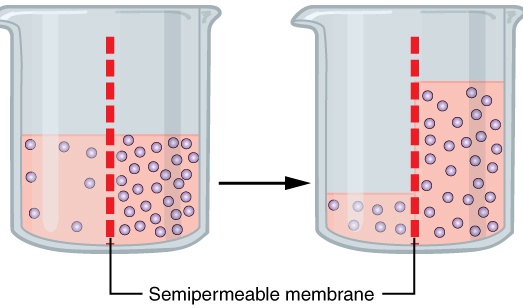
Osmosis
movement of water towards to more concentrated compartment
Oxidation
Chemical reaction with oxygen
Oxidative browning
Brown color on fruits and vegetables after exposure to air
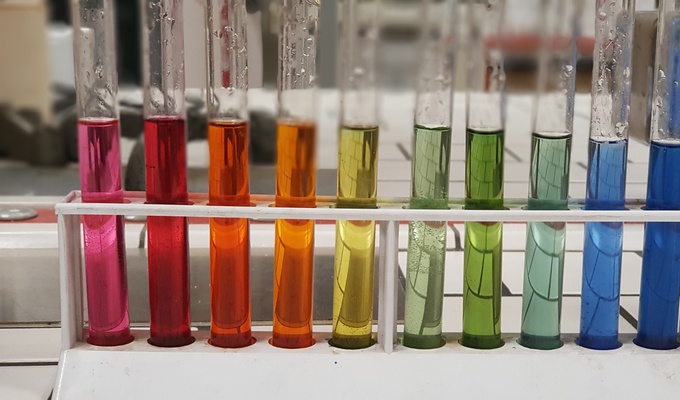

pH
measure of the acidity or basicity of an aqueous solution
Polyphenol oxidase
Enzyme responsible for fruit browning
Polyphenols
Naturally occuring compounds in plants
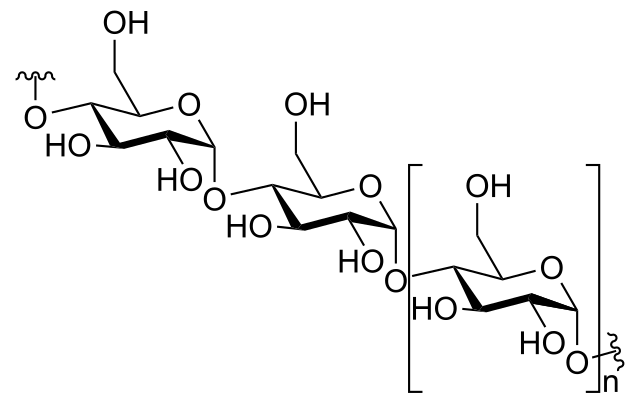
Polysaccharide
long chain of units of monosaccharide (carbohydrate)
Polyunsaturated fat
Dietary fat, typically fish or plant based, liquid at room temperature
Proof
Unit of alcohol content, equal to one-half percent
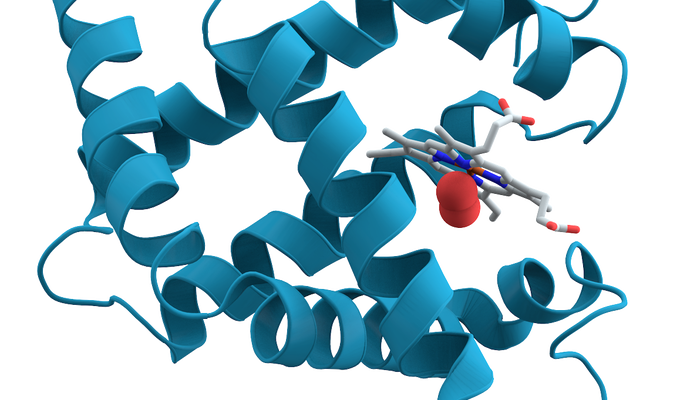
Protein
Large molecules found in all living cells
Psychoactive agent
chemical substance that affects brain function or perception
Quinone
Molecules reponsible for fruit and vegetable browning
Rancidity
Conversion of fats and oils into foul-tasting or -smelling substances
Ripening
Process of softening and sweetening in fruits
Safrole
Chemical compound occurring in sassafras
Saltpeter
Chemical used as preservative and curing agent for meats
Saturated fat
Dietary fat, associated with negative health effects
Sodium stearoyl lactylate
Chemical emulsifier added to processed foods
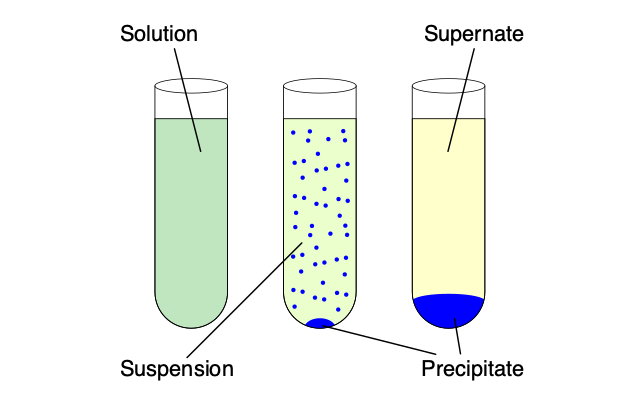
Solubility
capacity of a solid, liquid, or gaseous substance to dissolve in a solvent
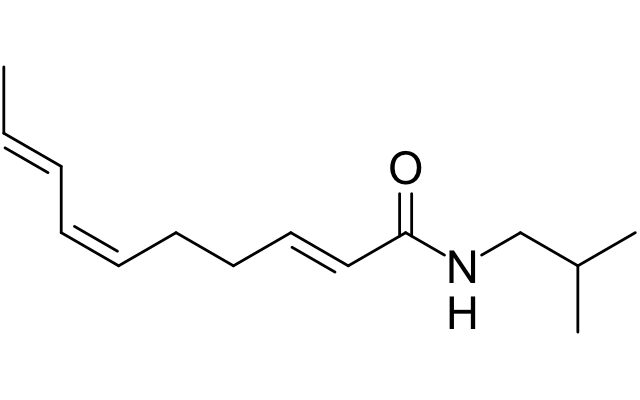
Spilanthol
chemical compound
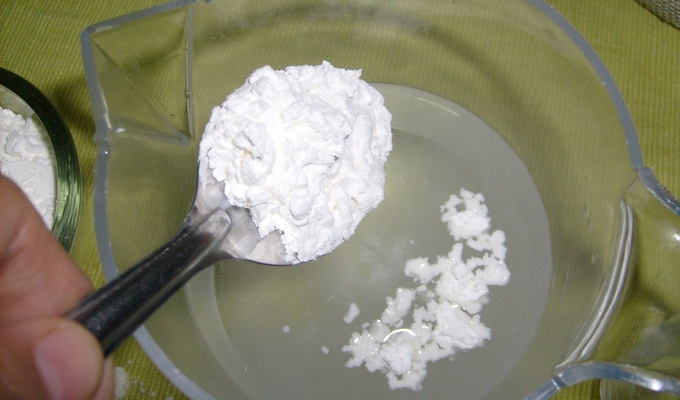

Starch
carbohydrate consisting of a large number of glucose units joined by glycosidic bonds
Sweet-smelling chemical
Tannin
Plant-based compounds that provide bitterness and astringency

Thickener
substance used to increase viscosity of a liquid
Toxic food
Trans fat
Chemically altered fat

Triglyceride
Chemical form of fats in the body and the diet

Umami
One of the five basic tastes
Vitamin
Volatile
Aromatic chemicals released from food
Subcategories:
Acetone
Acidifier
Acidulant
Acidulated water
Albumen
Alcohol by volume
Aldehyde
Alkalescents
Alkali
Alkali volatile
Alkaloid
Alpha-amylase
Amino acid
Amylase
Amylopectin
Amylose
Anthocyanin
Antioxidant
Arsenic
Artificial sweetener
Base
Brix
Butylated hydroxytoluene
Caffeine
Capsaicin
Carbohydrate
Cellulose
Coagulate
Coagulation
Coumarin
Cream of tartar
Curcumin
DATEM
Denature
Disaccharide
Emulsifier
Enzyme
Epimer
Essential oil
Extract
Fat
Fatty acid
Fiber
Flavonoid
Gliadin
Glutelin
Gluten
Humidity
Hydrogen cyanide
Hydrogenated
Hydrolyzed vegetable protein
Hygroscopic
Inversion
Invertase
Lactic acid
Lecithin
Lipid oxidation
Lye
Macronutrient
Maillard reaction
Menthol
Mixture
Modified starch
Mono- and diglycerides
Monosaccharide
Monounsaturated fat
Mucilage
Nigari
Nitrosamines
Oleuropein
Osmosis
Oxidation
Oxidative browning
Polyphenol oxidase
Polyphenols
Polysaccharide
Polyunsaturated fat
Proof
Protein
Psychoactive agent
Quinone
Rancidity
Ripening
Safrole
Saltpeter
Saturated fat
Sodium stearoyl lactylate
Solubility
Spilanthol
Starch
Sweet-smelling chemical
Tannin
Thickener
Toxic food
Trans fat
Triglyceride
Umami
Vitamin
Volatile
pH
Categories:
root-category
Also known as:
English:
Chemistry
Inbound Links
Unlinked Mentions
Article content licensed under CC-BY-SA
ID: 20148