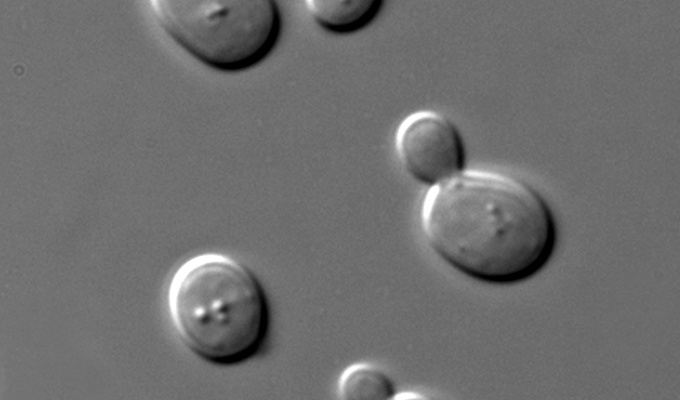
Yeasts are eukaryotic, single-celled microorganisms classified as members of the fungus kingdom. The first yeast originated hundreds of millions of years ago, and at least 1,500 species are currently recognized. They are estimated to constitute 1% of all described fungal species.
The yeast species Saccharomyces cerevisiae converts carbohydrates to carbon dioxide and alcohols through the process of fermentation. The products of this reaction have been used in baking and the production of alcoholic beverages for thousands of years.
Yeasts do not form a single taxonomic or phylogenetic grouping. The term "yeast" is often taken as a synonym for Saccharomyces cerevisiae, but the phylogenetic diversity of yeasts is shown by their placement in two separate phyla: the Ascomycota and the Basidiomycota. The budding yeasts or "true yeasts" are classified in the order Saccharomycetales, within the phylum Ascomycota.